Design & Technology

Summary
Design and Technology is available to all students at KS3, leading to potential pathways for GCSE and A Level. Students are taught on a rotation system of approximately 11 weeks, where they have an opportunity to experience different aspects of this broad and exciting subject across 3 lessons per fortnight.
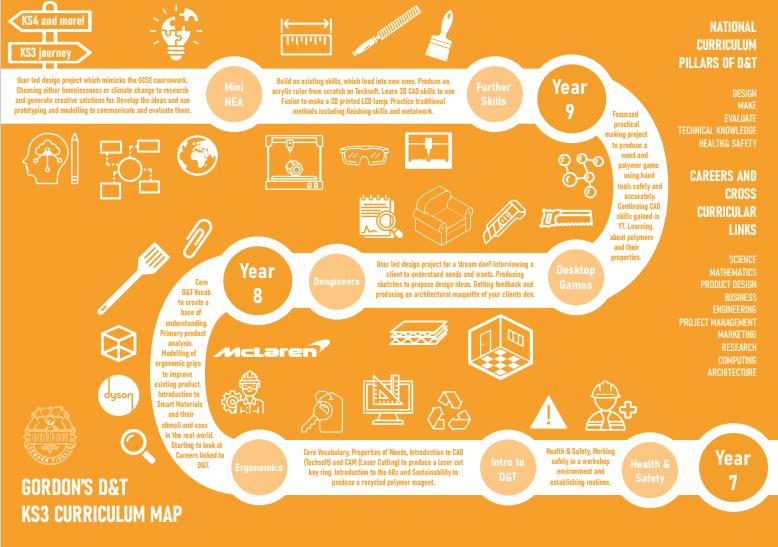
Year 7: Students will explore ergonomic design, and begin to make connections to the designed world around them. They will also begin to work on their design and 2D CAD skills, and learn about the importance of sustainability.
Year 8: Students undertake a user led design project, where they explore a real client's needs and wants, designing a solution that's right for them. Students will also begin to develop more traditional workshop in addition to their 2D CAD, processes to produce a wood and plastic tabletop game.
Year 9: At this stage, students have a firm grounding in DT, and will complete an iterative design project, responding to a contextual challenge to generate and develop meaningful solutions. In addition to this, they will also continue to hone their 2D CAD skills, and be introduced to industry standard 3D CAD software. Traditional workshop processes using wood and metals will also be utilised.
Our exciting curriculum has been carefully designed to give students the broadest base of knowledge and transferrable skills to take forward to a design career pathway or otherwise.
Head of Department: Ms Edwards aedwards@gordons.school

Summary
AQA Design and Technology GCSE: The new specification offers a broad look at designing products including end user requirements, environmental impacts, new and emerging technologies, the work of others, industrial design practice and a range of materials including Textiles/Graphics/Electronics and Resistant Materials. There is a large theory content with 50% of the GCSE grade being the exam and the rest the NEA (coursework). Students are required to independently progress their NEA portfolio and making.
Students are only able to choose one area of Design and Technology to study at GCSE.
Course details
Students should be advised that the significant NEA (coursework) element of the subject means that students must be self motivated, independent learners and are expected to put in significant effort outside of lesson time to be successful.
GCSE Design and Technology will prepare students to participate confidently and successfully in an increasingly technological world. Students will gain awareness and learn from wider influences on Design and Technology including historical, social, cultural, environmental and economic factors. Students will get the opportunity to work creatively when designing and making and apply technical and practical expertise. Our GCSE allows students to study core technical and designing and making principles, including a broad range of design processes, materials techniques and equipment. They will also have the opportunity to study specialist technical principles in greater depth.
TYPICAL ACTIVITIES:
Students will spend an almost equal amount of time on theory tasks and practical application, there is a significant amount of written work.
• materials and components
• design and market influences
• processes and manufacture
• the new specifications place a large emphasis on Science and Math’s within the course
• focus on creative strategies to enable different outcomes
The exams and non-exam assessment will measure how students have achieved the following assessment objectives.
AO1: Identify, investigate and outline design possibilities to address needs and wants.
AO2: Design and make prototypes that are fit for purpose.
AO3: Analyse and evaluate: design decisions and outcomes, including for prototypes made by themselves and others, wider issues in design and technology.
AO4: Demonstrate and apply knowledge and understanding of:
• technical principles
• designing and making principles.
50% Externally marked exam.
50% Internally marked Controlled Assessment - Written folder of approximately 24 x A3 digital portfolio pages.

Summary
This course is examined at the end of Year 13 and on the NEA (Non Exam Assessment) portfolio.
This creative and thought-provoking qualification gives students the practical skills, theoretical knowledge and confidence to succeed in a number of careers. They will investigate historical, social, cultural, environmental and economic influences on design and technology, whilst enjoying opportunities to put their learning in to practice by undertaking their own iterative design process and by producing prototypes of their choice as part of the NEA.
Theory topic are as follows:
Units 1-4: Performance characteristics of papers and boards, polymers, woods and metals;
Unit 5: Composite, smart and modern materials;
Units 6-9: Processing and working with papers and boards, polymers, woods and metals;
Unit 10: Modern industrial and commercial practice
Unit 11: Product design considerations
Unit 12: Product design and development
Unit 13: Design methods
Unit 14: Design processes
Course details
Technical Principles: The focus is on the physical and mechanical properties of a range of materials and components and why these are used in specific applications, with emphasis on the life-cycle of products. This includes manufacture, use and disposal plus an understanding of the methods by which materials and components can be manipulated to manufacture products. The NEA provides an opportunity for students to learn about CAD and CAM, and the use of basic quality control measures.
Designing and making principles: Through study and detailed analysis of a wide range of products, candidates should begin to develop knowledge and understanding of the broader issues for the designer such as: environmental sustainability of products and their manufacture, ergonomics and anthropometrics, inclusive design, and consumer safety.
Entry Criteria
GCSE grade 6 in Technology if studied or GCSE grade 5 in Mathematics is required.
/_site/data/files/curriculum/curriculum-maps/dt/DF679CF4CA44BBB87DB47B6AC79BDD25.pdf